Introduction to Google BigQuery
Overview of Google BigQuery
Google BigQuery is a fully managed, serverless, and highly scalable data warehouse that enables efficient analysis of large datasets using SQL. Designed to simplify the process of querying massive datasets, BigQuery allows businesses to process data in real time, gaining insights quickly and easily without the need to manage infrastructure. With its pay-as-you-go model, users only pay for the amount of data processed, which makes it a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes. Whether you’re working with gigabytes or petabytes of data, BigQuery offers seamless scaling to meet your data needs.Key Features and Use Cases
- Serverless Architecture
- Scalable and Fast Data Processing
- SQL-Like Queries
- Machine Learning Integration
- Real-Time Analytics
- Data Security and Governance
BigQuery operates without requiring users to manage servers or infrastructure. This serverless nature means Google handles all backend tasks, such as infrastructure provisioning, scaling, and performance optimization, allowing users to focus on analyzing their data.
BigQuery excels in handling large datasets. Whether you’re analyzing terabytes or petabytes, the platform’s distributed architecture ensures rapid query execution. Google’s Dremel technology is the backbone of BigQuery, allowing for fast SQL queries across massive datasets.
BigQuery supports SQL, the widely-used query language, making it accessible to data analysts and professionals familiar with SQL. Additionally, it integrates with multiple data visualization and analysis tools like Looker, Tableau, and Google Data Studio, simplifying data exploration and reporting.
BigQuery ML (Machine Learning) lets users create and run machine learning models using standard SQL queries, without needing to move data or learn complex programming languages. This feature makes it possible to perform predictive analysis directly within the BigQuery environment.
BigQuery can ingest streaming data and provide real-time analysis, making it ideal for use cases such as monitoring real-time user interactions on a website, tracking IoT sensor data, or evaluating live financial transactions.
BigQuery offers robust security features, including encryption at rest and in transit, Identity and Access Management (IAM) for user control, and data loss prevention tools. These features ensure compliance with industry regulations and protect sensitive data.
Common Use Cases
Setting Up BigQuery on Google Cloud
To get started with BigQuery, you’ll need a Google Cloud account. Here’s a step-by-step guide to setting up BigQuery:
Step 1: Create a Google Cloud Account
If you don’t already have a Google Cloud account, visit Google Cloud Console and sign up. New users typically get free credits that can be used to explore various Google Cloud services, including BigQuery.
Step 2: Enable BigQuery API
Once you have an account, go to the Google Cloud Console and navigate to the “APIs & Services” dashboard. Search for "BigQuery API" and enable it. Enabling the API allows you to interact with BigQuery through the console or programmatically via API requests.
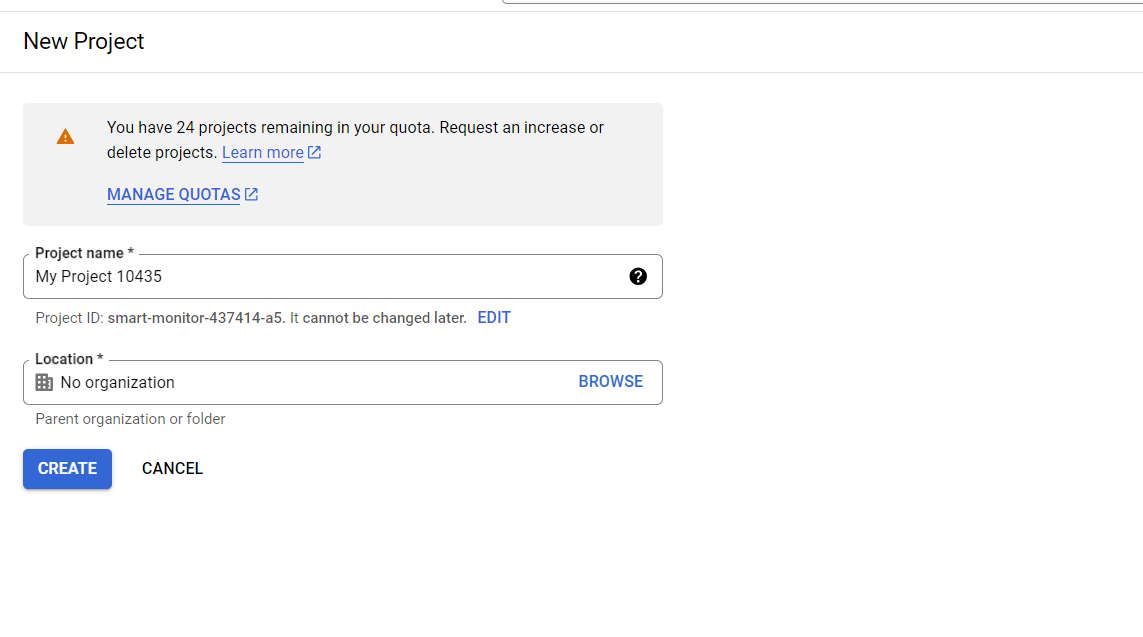
Step 3: Create a Project
In Google Cloud, every action occurs within a project. You can create a new project from the Google Cloud Console:
Step 4: Open BigQuery Console
Once your project is created, access BigQuery by navigating to the BigQuery console. Here, you can start creating datasets, importing data, and running SQL queries.
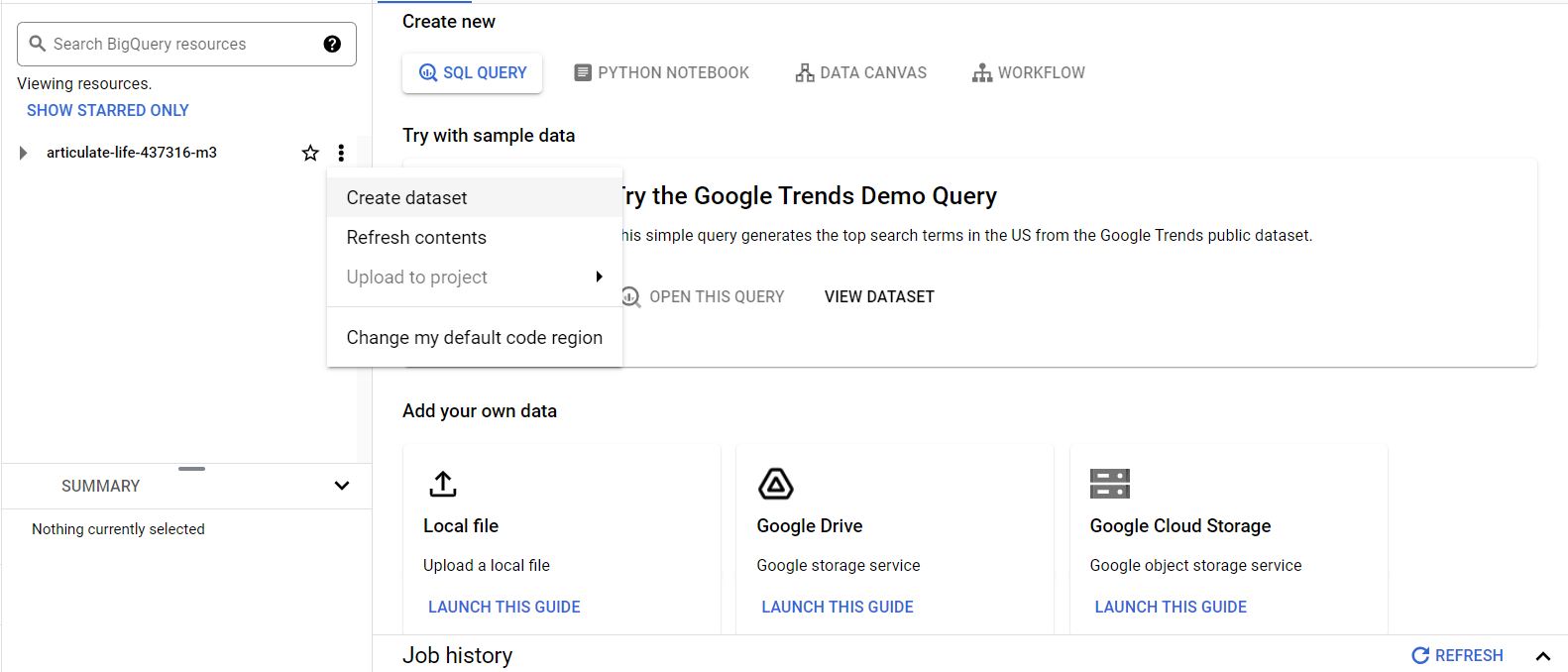
Step 5: Create a Dataset
Datasets in BigQuery are collections of tables. To create a dataset:
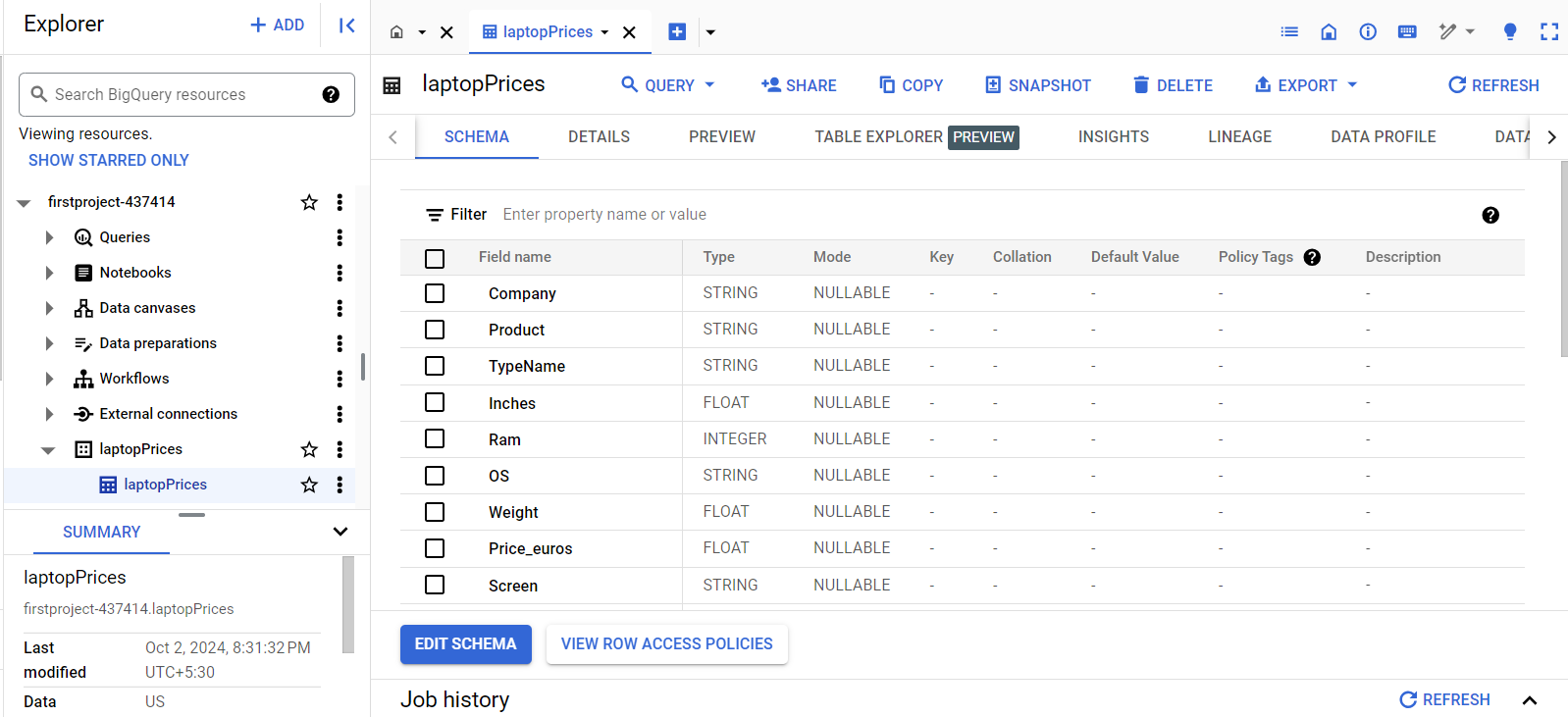
Step 6: Load Data into BigQuery
You can load data into BigQuery from various sources:
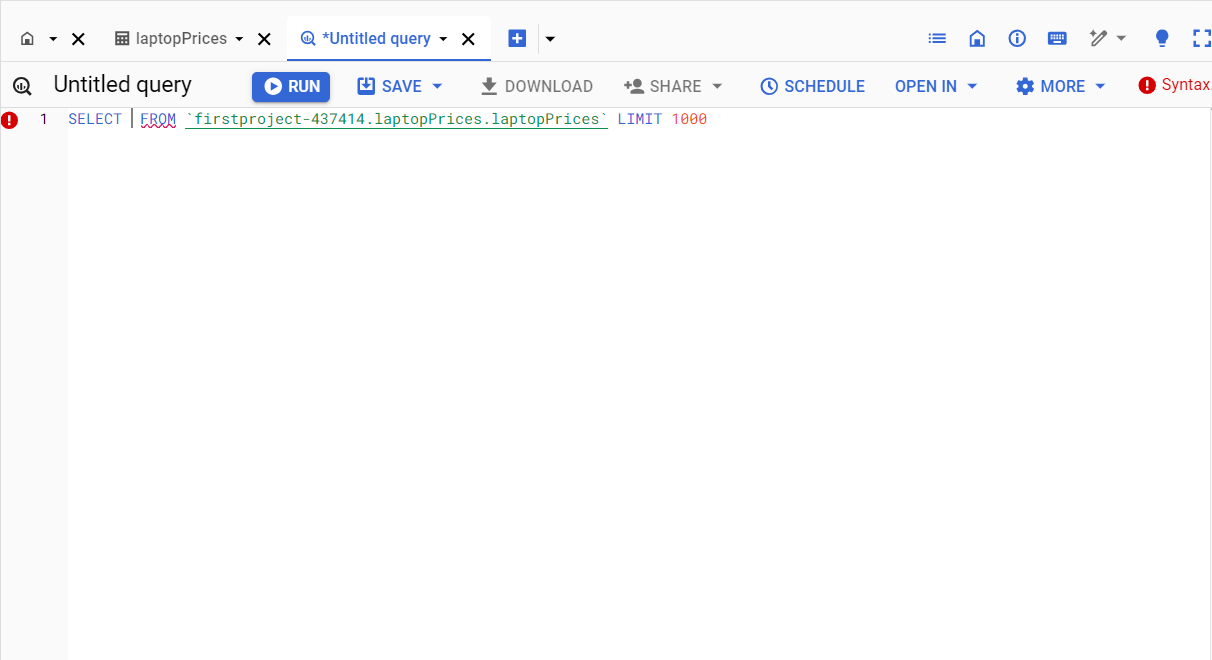
Step 7: Run Queries
Once your data is loaded, you can start running SQL queries. BigQuery provides a SQL workspace in the console where you can write and execute queries.