Viewing and Inspecting Data
Why View and Inspect Data?
Before performing any data analysis or manipulation, it's crucial to understand the dataset. Viewing and inspecting the data serves the following purposes:- Identify missing values.
- Understand data types and distributions.
- Detect outliers and anomalies.
- Gain insights into the overall structure and content of the dataset.
Viewing Data with head() and tail()
The head() and tail() methods are among the first functions you'll use when working with a DataFrame. They allow you to view the first and last few rows of the dataset, respectively.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('/content/Car data.csv')
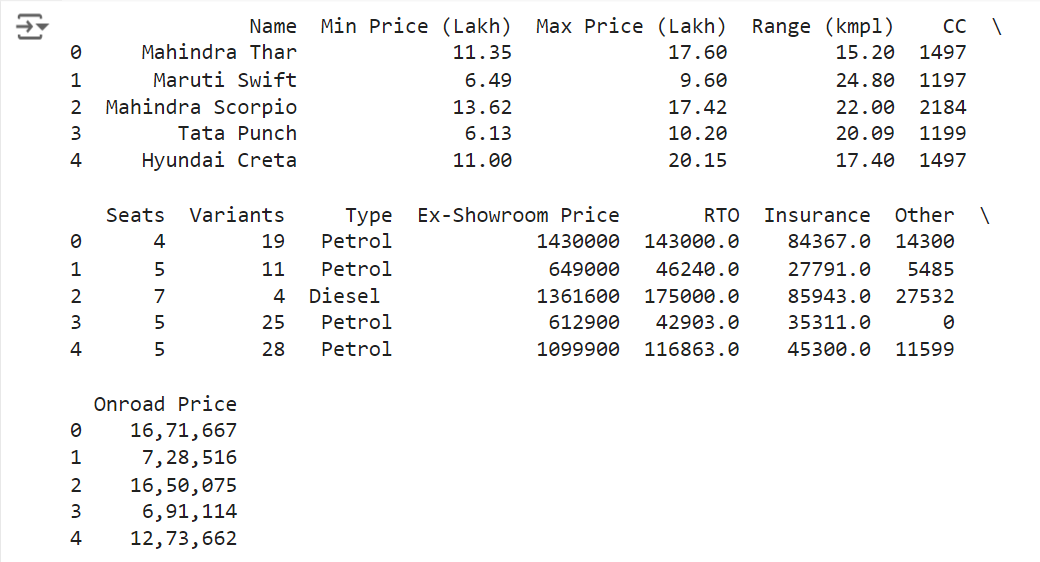
# Viewing the first 5 rows
print(df.head())
Output
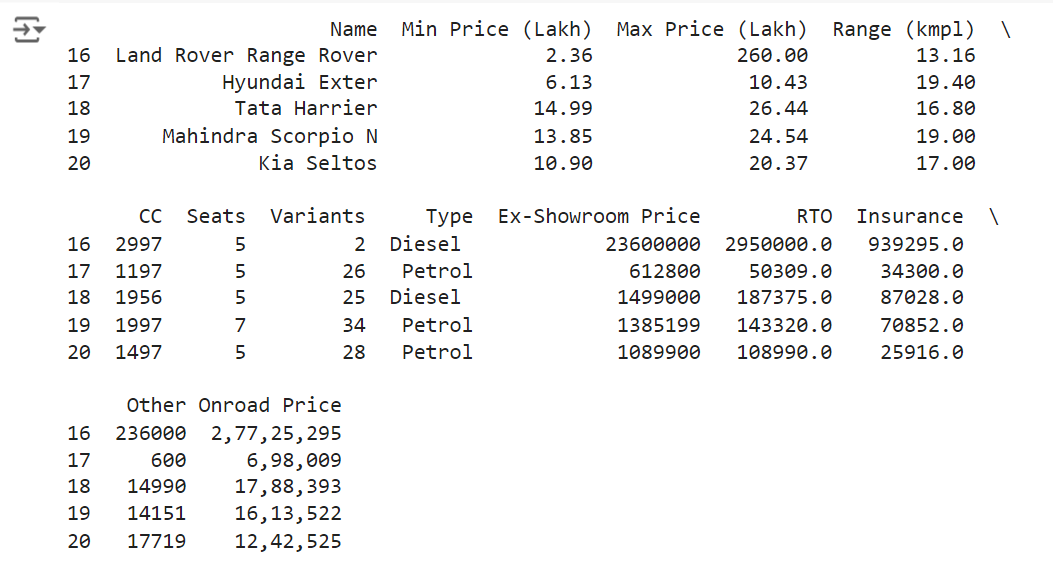
# Viewing the last 5 rows print(df.tail())
Output
Inspecting Data with info() and describe()
To get a more detailed understanding of your data, the info() and describe() methods are invaluable.
info() Method
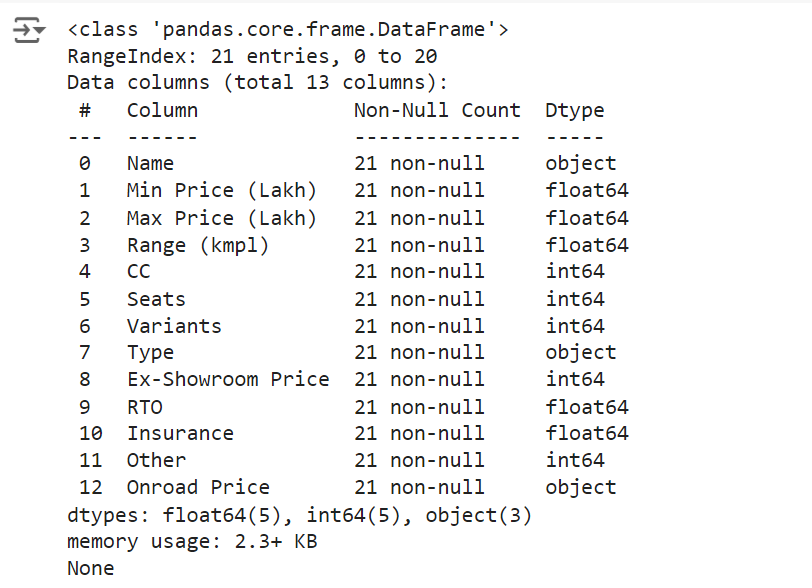
The info() method provides a concise summary of the DataFrame, including the number of entries, data types, and non-null counts.
# Get a concise summary of the DataFrame print(df.info())
Output
describe() Method
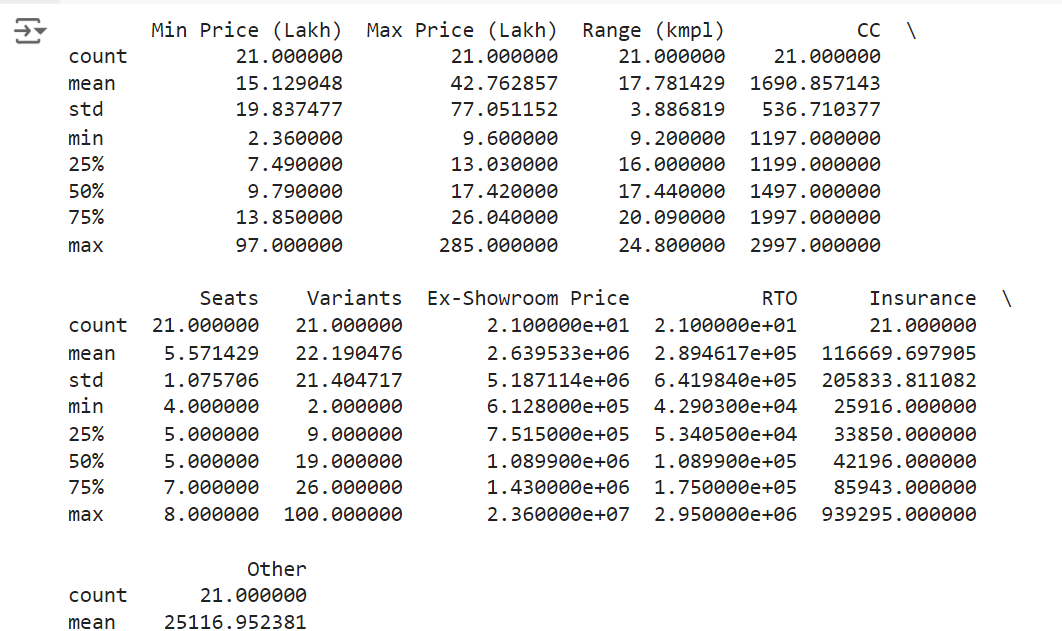
The describe() method offers a statistical summary of your numerical columns, including metrics like mean, standard deviation, minimum, and maximum values.
# Get a statistical summary of the DataFrame print(df.describe())
Output